Introduction
In Windows Server, Active Directory (AD) relies on Flexible Single Master Operations roles to maintain its integrity and proper function. These roles are divided into forest-wide and domain-specific functions. Knowing which domain controller holds each FSMO role is crucial for AD administration.
This blog post will guide you how to identify the DCs responsible for the Domain Naming Master and Schema Master roles, as well as how to view domain-specific FSMO roles.
What Are FSMO Roles?
Operations Master Roles, also known as Flexible Single Master Operations (FSMO) Roles, are critical for maintaining the consistency and stability of Active Directory environment. FSMO roles are initially assigned to the first domain controller in the domain or forest.
In addition, FSMO roles are single-master to prevent conflicts and maintain consistency. We have Forest-wide FSMO roles and Domain-specific FSMO roles:
Forest-wide FSMO Roles
Forest-wide FSMO roles are special Domain Controller (DC) roles in Active Directory that affect the entire forest. There are two forest-wide FSMO roles:
Schema Master
- Scope: Forest-level role.
- Responsibilities:
- Manages the Active Directory schema, which defines the structure of the directory, including attributes and classes of objects.
- Controls schema modifications, such as adding attributes or classes.
- Default Location: The first domain controller in the forest root domain.
Domain Naming Master
- Scope: Forest-level role.
- Responsibilities:
- Manages changes to the domain namespace, ensuring all domain names are unique within the forest.
- Control the addition and removal of child domains within the forest.
- Default Location: The first domain controller in the forest root domain.
Domain-specific FSMO Roles
Relative ID (RID) Master
- Scope: Domain-level role.
- Responsibilities:
- Allocates Relative ID (RID) pools to other domain controllers in the domain.
- RIDs are appended to the domain’s identifier to create unique Security Identifiers (SIDs) for AD objects like users, groups, and computers.
- Default Location: The first domain controller in the domain.
Primary Domain Controller (PDC) Emulator
- Scope: Domain-level role.
- Responsibilities:
- Acts as the time source for the domain to ensure Kerberos authentication functions correctly. It synchronize time for all computers within the domain.
- Handles password changes and user authentication across the domain.
- Provides backward compatibility for older systems and applications that rely on the concept of a Primary Domain Controller (PDC).
- Default Location: The first domain controller in the domain.
Infrastructure Master
- Scope: Domain-level role.
- Responsibilities:
- Tracks and updates cross-domain references within a multi-domain environment, ensuring that references to objects (e.g., users or groups) in other domains remain consistent.
- Especially critical in environments with multiple domains and when users or groups reference objects in other domains.
- Default Location: The first domain controller in the domain.
Lab Topology
Before guiding you how to identifying Forest-wide and Domain-Specific FSMO Roles, take a look at the lab setup (techexample.local):
| Server | IP Address | Default Gateway |
| DC01 | 192.168.1.100 | 192.168.1.254 |
| WS01 (Secondary DC) | 192.168.1.101 | 192.168.1.254 |
To learn how to setup this lab, go here.
Let’s continue!
Identify which Domain Controller Holds Schema Master Role
Just a reminder, only one DC in the forest can hold the Schema Master role at a time. Here are the steps to identify:
Step 1: Register the Schema Management Console
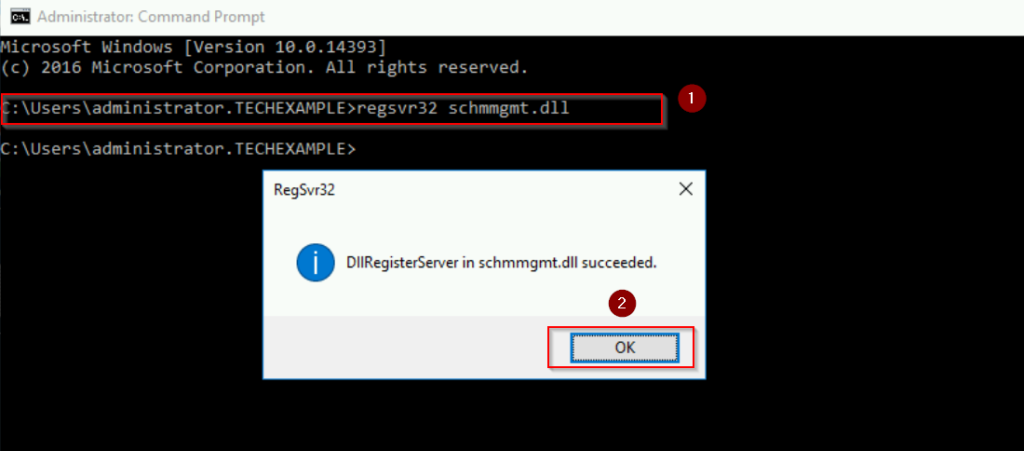
- Log in to WS01, open Command Prompt and type the following:
regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll
- Press Enter and click OK.
Step 2: Open Microsoft Management Console (MMC)
- After registering the Schema Management snap-in, type mmc in the Command Prompt and press Enter to open the MMC.
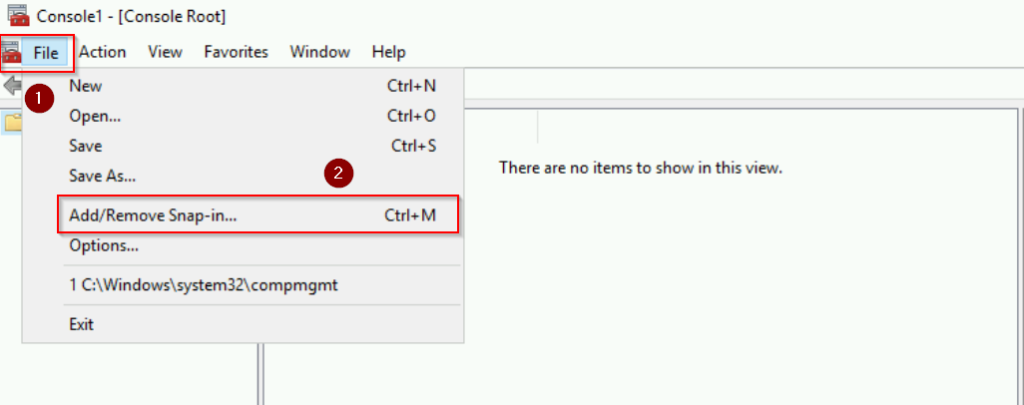
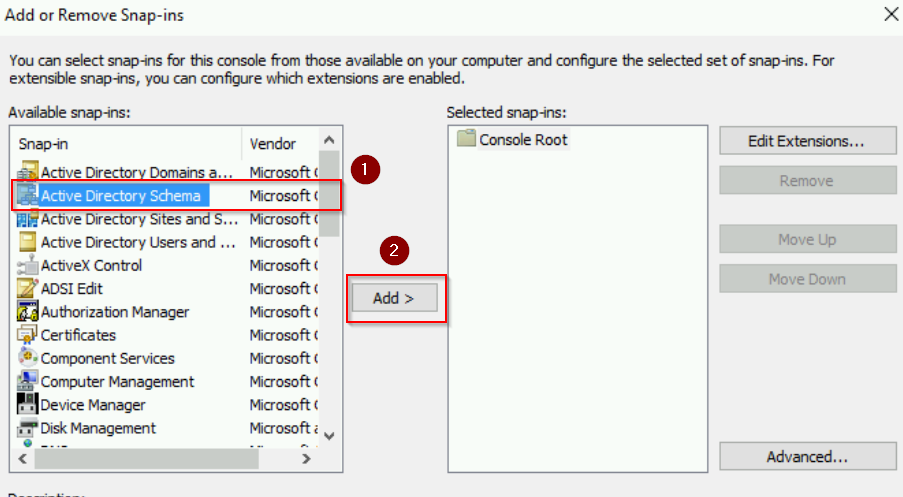
Step 3: Add the Active Directory Schema Snap-In
- In the MMC, click on File > Add/Remove Snap-in.
- Choose Active Directory Schema and click Add.
- Click OK to close the snap-in window.
Step 4: Check the Schema Master Role
- Right-click Active Directory Schema in the MMC and select Operations Master. The Schema master role holder will be displayed here. In this case, the “Current schema master (online)” shows VM-DC01.techexample.local. The server VM-DC01 is currently reachable and functioning.
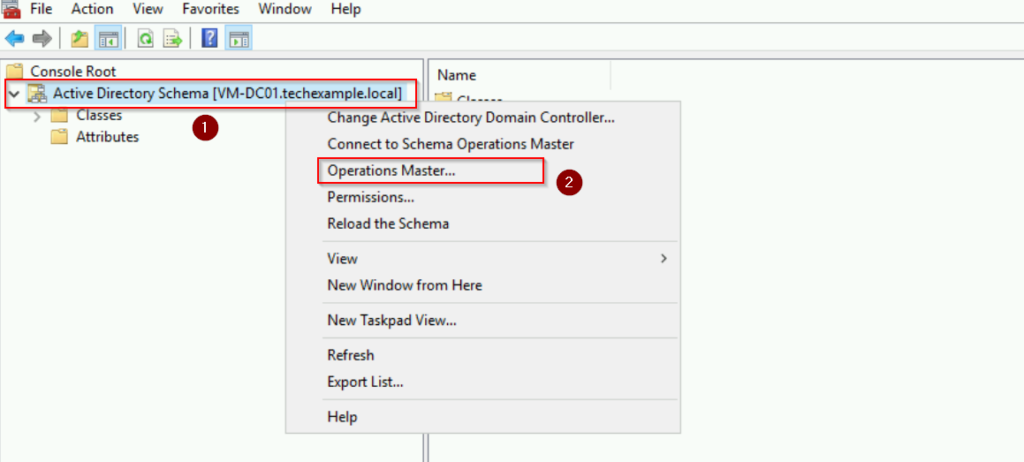
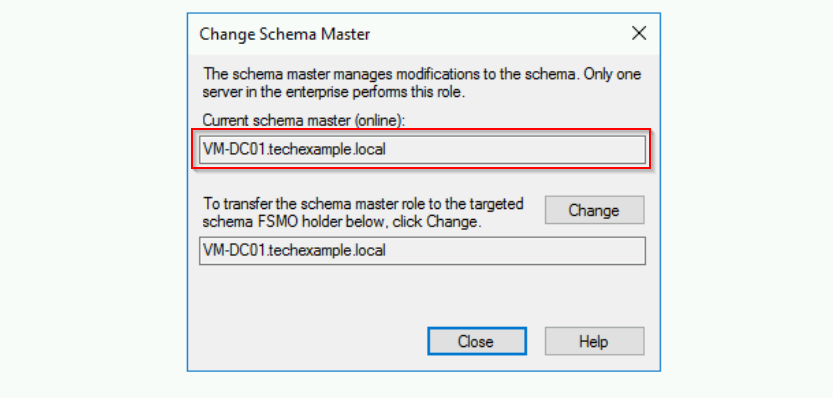
Notice that both boxes show the same server name indicates that no role transfer is currently being performed.
Identify which Domain Controller Holds Domain Naming Master Role
The Domain Naming Master role ensures no naming conflicts when adding or deleting domains. Below are the steps how to view it:
- We are still in WS01 server. Go to Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Domains and Trusts
- Right-click the top node (techexample.local) and select Operations Master
- In the Operations Master window, you will see the Domain Naming Master role displayed. The domain controller that currently holds this role will be listed.
See screenshots below:

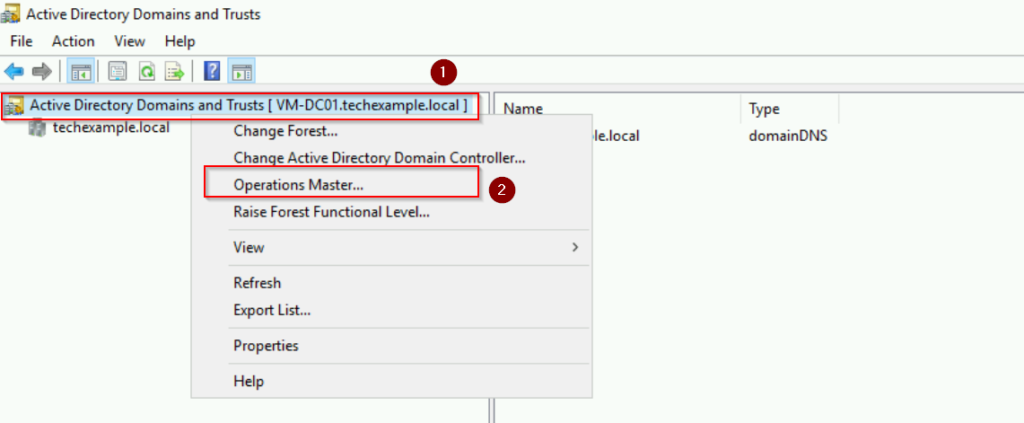

As you can see, the server VM-DC01.techexample.local is currently the Domain Naming Master for the AD forest.
How to view Domain-specific FSMO roles
Now, we are moving to view the Domain-specific roles: RID Master, PDC Emulator and Infrastructure Master.
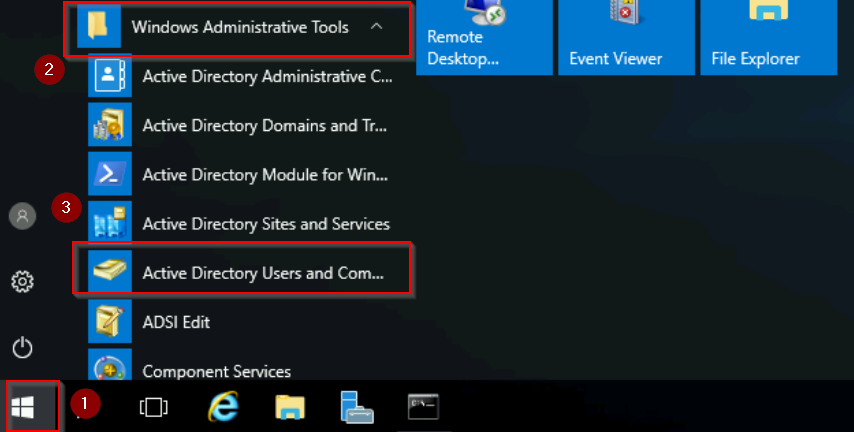
- In WS01 server, go to Start > Administrative Tools > Active Directory Users and Computers.
- Right-click your domain and select Operations Master.
- In the Operations Master dialog, you will see three tabs:
- RID: Displays the current holder of the RID Master role.
- PDC: Displays the current holder of the PDC Emulator role.
- Infrastructure: Displays the current holder of the Infrastructure Master role.
Here are the screenshots:
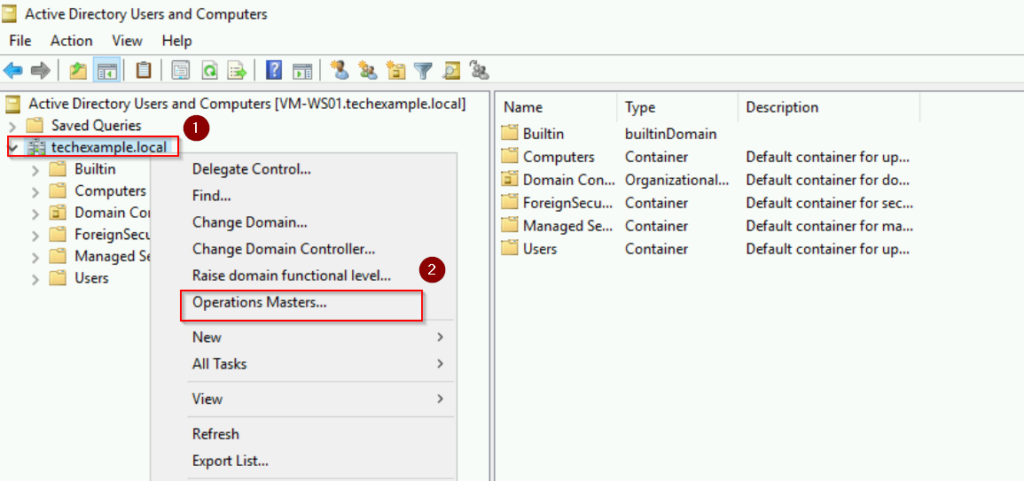
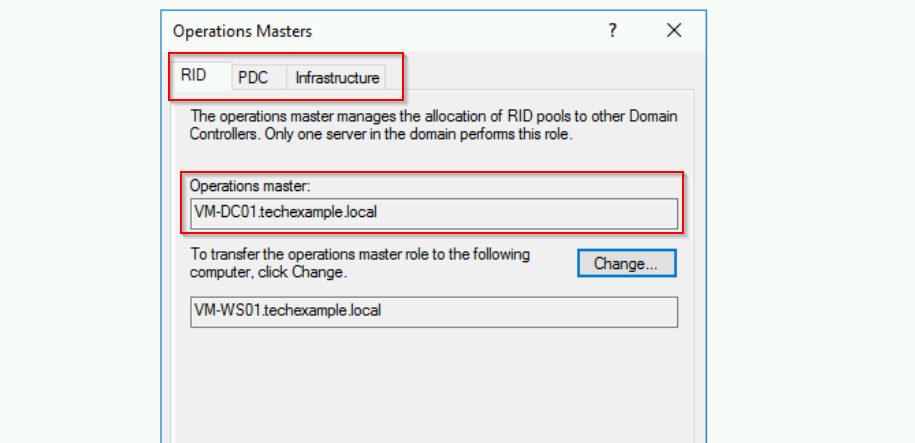
If you click on each tab, you will see the current Operation Master role is held by VM-DC01. This server is in the techexample.local domain.
Conclusion
To sum up, we’ve focused on viewing FSMO role holders, which is the first step before any potential transfer or troubleshooting. Being aware of these roles and knowing how to view them will help you maintain a healthy and functional Active Directory infrastructure.
Stay tuned for our next blog, where we will dive into how to transfer FSMO roles when needed.
